Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is an aggressive form of cancer that poses significant challenges for patients and healthcare providers alike. With limited treatment options available, the search for innovative therapies continues.
In recent years, immunotherapy has emerged as a promising approach in cancer treatment, offering new hope for patients with SCLC.
Overview of Small Cell Lung Cancer and Its Impact on Patients
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is a highly aggressive form of lung cancer that accounts for approximately 15% of all cases. Unlike non-small cell lung cancer, which tends to grow more slowly, SCLC is characterized by fast-growing tumors that have a propensity to spread rapidly to other parts of the body.
This aggressive nature makes it particularly challenging to treat and has contributed to its high mortality rate.
The impact of SCLC on patients is profound. As the disease progresses, patients often experience symptoms such as persistent coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain, and unintentional weight loss. These symptoms can significantly impact their quality of life and overall well-being.
In addition to the physical symptoms, the emotional toll of living with a diagnosis of small cell lung cancer can be overwhelming for both patients and their loved ones.
Given the aggressive nature of SCLC and its tendency to spread quickly, early detection is crucial for improving treatment outcomes. However, SCLC is often diagnosed at an advanced stage when treatment options are limited. The urgent need for more effective treatments remains a pressing concern in the medical community.
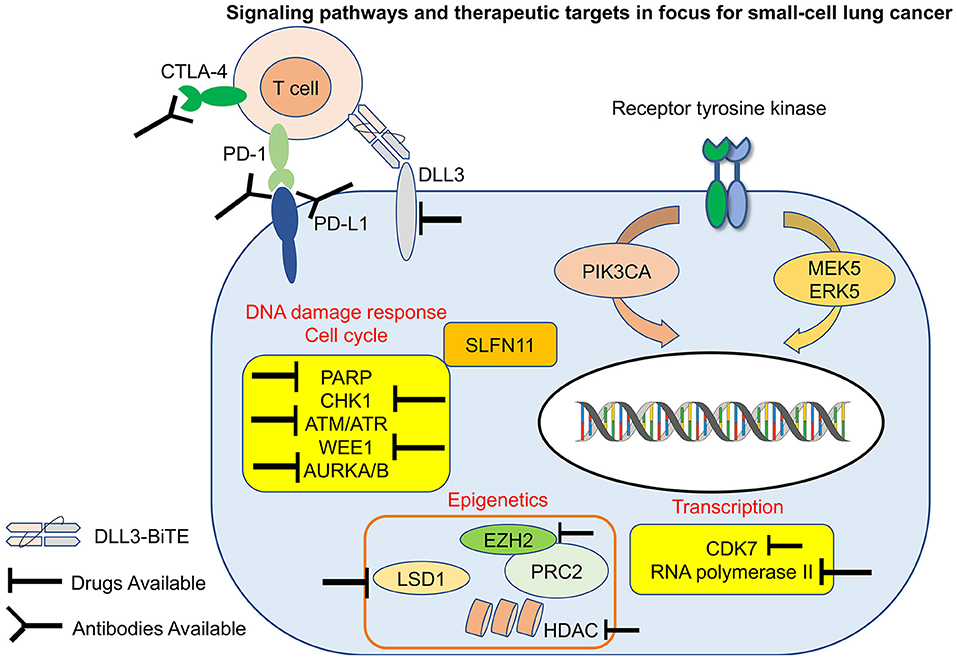
In recent years, advancements in targeted therapies and immunotherapies have shown promise in treating certain types of lung cancer. However, these treatments are still being studied for their effectiveness specifically in small cell lung cancer cases.
Clinical trials are underway to explore new treatment options and improve survival rates for SCLC patients.
In conclusion, small cell lung cancer poses unique challenges due to its aggressive nature and propensity for rapid spread. The impact on patients is significant both physically and emotionally.
Continued research efforts are focused on developing more effective treatments that can improve outcomes for individuals diagnosed with this devastating disease.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
Limitations and Challenges with Current Treatment Options
Traditional treatments for small cell lung cancer (SCLC) such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy provide temporary relief but often fail to deliver long-term benefits. These treatments can cause severe side effects, impacting patients’ quality of life.
Therefore, there is an urgent need to explore alternative approaches that offer better outcomes with fewer adverse effects.
Immunotherapy is a groundbreaking approach in cancer treatment that utilizes the body’s immune system to fight against cancer cells. Unlike traditional treatments that directly target tumor cells, immunotherapy enhances the body’s natural defenses to recognize and destroy cancer cells.
It offers advantages such as durable responses, long-term remission rates, and better tolerance compared to chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
By understanding the limitations of current treatment options for SCLC and exploring the potential of immunotherapy, we can pave the way for more effective and less toxic therapies for patients.
Introduction to Immunotherapy and Its Mechanism of Action
Immunotherapy is a revolutionary approach in cancer treatment that utilizes checkpoint inhibitors or monoclonal antibodies to block specific proteins on immune or cancer cells. By targeting these checkpoints, immunotherapy enhances the immune system’s ability to attack and eliminate cancer cells.
Unlike traditional treatments, immunotherapy focuses on empowering the body’s natural defenses rather than directly targeting the tumor itself. This groundbreaking approach offers long-lasting effects and shows promise across various types of cancers.
With ongoing research and development, immunotherapy continues to provide new hope for patients battling cancer.
Key Benefits and Advantages of Immunotherapy over Traditional Treatments
Immunotherapy presents a myriad of key benefits and advantages that set it apart from traditional treatments for cancer. One major advantage lies in its ability to produce durable responses even after treatment discontinuation.
Unlike chemotherapy, which often requires continuous administration, immunotherapy can stimulate the immune system to remember and recognize cancer cells, providing long-term protection against disease recurrence.
Furthermore, immunotherapy offers a more targeted approach that minimizes damage to healthy cells and reduces the risk of debilitating side effects commonly associated with traditional treatments. By harnessing the power of the body’s own immune system, immunotherapy can selectively target cancer cells while sparing healthy tissues.
Another significant advantage of immunotherapy is its versatility in treating various types of cancer, including small cell lung cancer (SCLC). It has shown promising results in combating this aggressive form of lung cancer. One notable breakthrough in SCLC treatment is Tecentriq (atezolizumab), an innovative immunotherapy developed by Roche.
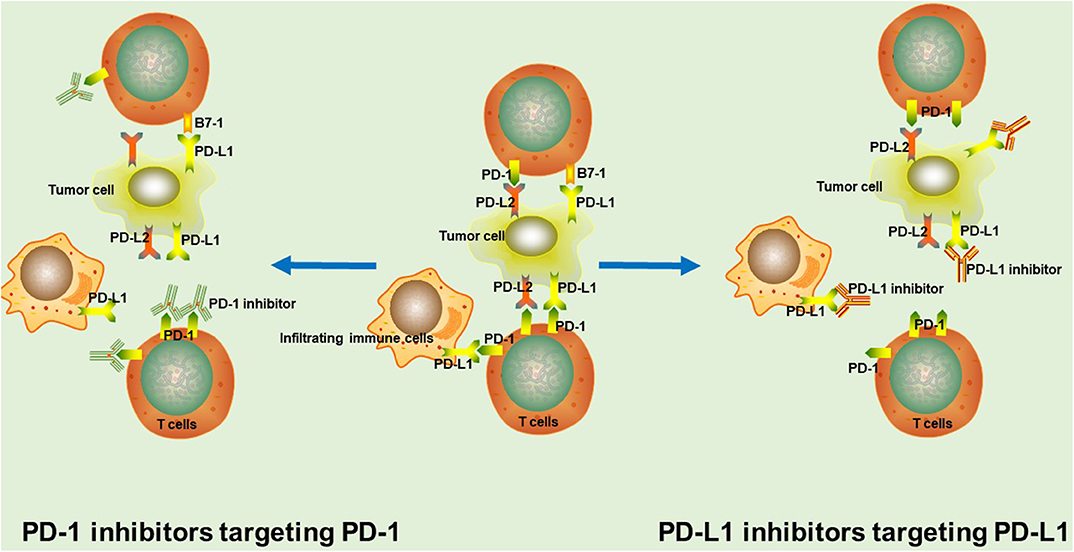
Tecentriq works by blocking the PD-L1 protein on cancer cells, thus allowing the immune system’s T-cells to detect and attack them. This targeted approach not only enhances the efficacy of treatment but also reduces the risk of collateral damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
In summary, immunotherapy showcases several key benefits and advantages over traditional treatments for cancer. Its ability to induce durable responses, minimize harm to healthy cells, and treat various types of cancer makes it a promising option for patients seeking effective and personalized therapies.
With ongoing advancements in immunotherapeutic approaches like Tecentriq, we are witnessing an exciting evolution in the field of oncology that holds great promise for improved patient outcomes.
Brief Explanation of Tecentriq and How it Differs from Other Immunotherapies
Tecentriq is a unique immunotherapy that stands out from others due to its specific mechanism of action. While many immunotherapies target the PD-1 pathway, Tecentriq specifically targets PD-L1 on cancer cells. This distinction makes it effective for patients with high PD-L1 levels in their tumors.
By blocking the interaction between PD-L1 and immune cells’ receptors, Tecentriq unleashes the immune system to better recognize and attack cancer cells. Its precision minimizes side effects, allows for combination therapies, and overcomes resistance mechanisms. Tecentriq offers a promising option for improving outcomes in cancer treatment.
FDA Approval of Tecentriq for Small Cell Lung Cancer
In March 2019, a significant milestone was achieved in the treatment of extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) with the accelerated approval of Tecentriq by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
This groundbreaking decision provided new hope for patients facing limited choices in their battle against this aggressive form of lung cancer.
Tecentriq, an immunotherapy drug developed by Genentech, has revolutionized the treatment landscape for ES-SCLC. Unlike traditional treatments, which often involve chemotherapy or radiation therapy, Tecentriq works through a different mechanism of action, harnessing the power of the body’s immune system to fight cancer cells.
By targeting a protein called PD-L1 on tumor cells and immune cells, Tecentriq helps to restore and boost the body’s natural defenses against cancer. This novel approach not only offers an alternative to standard treatments but also represents a significant advancement in SCLC treatment options.
The efficacy data supporting the FDA approval of Tecentriq in ES-SCLC patients is compelling. Clinical trials have demonstrated its ability to improve overall survival rates compared to chemotherapy alone.
In one study, patients who received Tecentriq in combination with chemotherapy experienced a median overall survival of 12.3 months, while those who received chemotherapy alone had a median overall survival of 10.3 months.
Additionally, Tecentriq has shown favorable results in terms of progression-free survival and response rates when compared to standard treatments. These findings further reinforce its potential as a game-changing therapy for ES-SCLC patients seeking effective and well-tolerated options.
The FDA’s accelerated approval of Tecentriq for ES-SCLC marks a significant turning point in the fight against this devastating disease.
As researchers continue to explore its full potential and refine treatment protocols, it is hoped that Tecentriq will continue to improve outcomes and provide new avenues for patients who previously had limited options.
How Tecentriq Works Against Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells
Tecentriq, an immunotherapy drug, targets small cell lung cancer cells by blocking the interaction between PD-L1 on cancer cells and PD-1 receptors on immune cells. This restores T-cells’ ability to recognize and attack cancer cells, slowing tumor growth.
Tecentriq’s targeted approach offers a promising alternative to traditional treatments for small cell lung cancer. It has received FDA approval in combination with chemotherapy as an initial treatment for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer.
Overview of Clinical Trials Involving Tecentriq in Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients
Clinical trials evaluating the efficacy of Tecentriq in small cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients have shown promising results. These trials specifically focused on patients with extensive-stage SCLC who had previously undergone chemotherapy.
The primary goal was to determine the effectiveness of Tecentriq in prolonging survival and improving overall response rates.
In terms of study design and patient population, the clinical trials included individuals who had received chemotherapy as their initial treatment. Tecentriq was then administered as a second-line therapy.
This approach allowed researchers to assess the impact of Tecentriq on various efficacy outcomes such as response rate, progression-free survival, and overall survival.
The results from these trials revealed significant benefits associated with using Tecentriq as a second-line treatment for SCLC. Compared to conventional treatments alone, Tecentriq demonstrated improved overall response rates and extended both progression-free survival and overall survival.
These findings highlight the potential value of incorporating Tecentriq into the existing treatment options for SCLC patients.
While it is essential to recognize the promising results offered by Tecentriq in SCLC treatment, it is equally important to understand its safety profile and manage any potential side effects effectively.
By comprehensively analyzing its safety profile, healthcare professionals can ensure that patients receive optimal care while undergoing treatment with Tecentriq.
To summarize, clinical trials investigating the use of Tecentriq in small cell lung cancer patients have shown encouraging results. By assessing its efficacy outcomes and understanding its safety profile, researchers aim to establish Tecentriq as a valuable addition to the current treatment arsenal for SCLC.
[lyte id=’oDiemaUov1Q’]