In recent years, the field of cancer treatment has witnessed a revolutionary breakthrough with the advent of immunotherapy. One key player in this rapidly evolving landscape is PD-1 agonist antibodies, which have shown immense potential in harnessing the power of our immune system to fight cancer.
For readers with an interest in investing and learning about the world of oncology, this article will provide a comprehensive overview of PD-1 agonist antibodies, their mechanism of action, current applications, limitations, and future perspectives.
Get ready to dive into the cutting-edge realm of immunotherapy and discover how PD-1 agonist antibodies are transforming the way we approach cancer treatment.
Understanding the Basics of Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a groundbreaking cancer treatment that harnesses our immune system’s power to fight cancer cells. Unlike traditional approaches like chemotherapy, it enhances our natural defenses.
By stimulating specific immune components or removing inhibitory signals, immunotherapy empowers our body to recognize and destroy cancer cells more effectively.
This targeted approach minimizes side effects and improves patients’ quality of life. Different strategies, such as using antibodies or activating T-cells, are employed in immunotherapy. Checkpoint inhibitors block immune checkpoints, allowing a stronger attack against cancer.
Immunotherapy not only treats tumors but also shows promise as a preventive measure through vaccine development. Understanding the basics of immunotherapy offers hope and opens up new possibilities in the fight against cancer. Ongoing research continues to reveal its potential for saving lives and improving outcomes for patients and their families.
The Role of PD-1 in Immune System Regulation
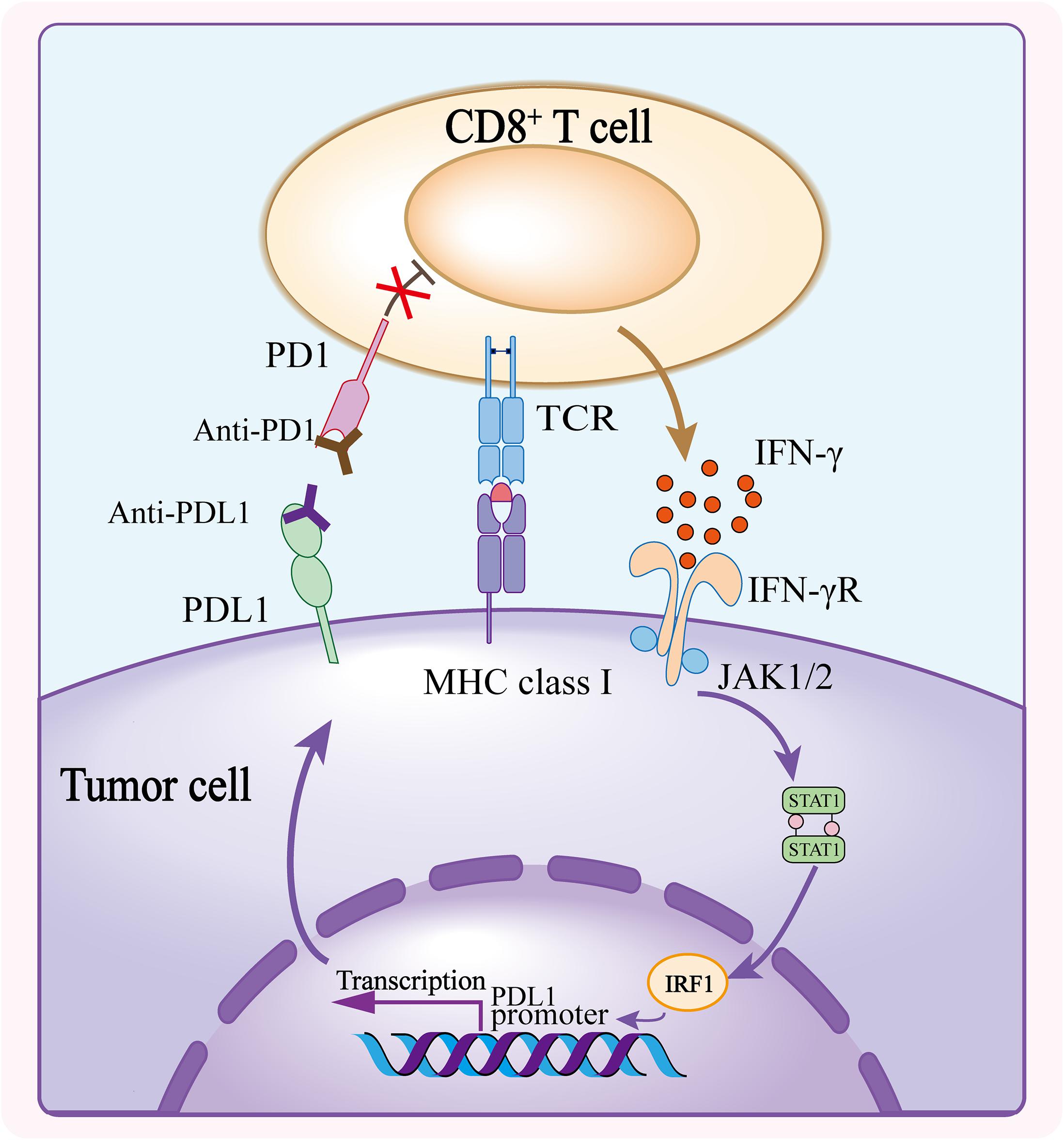
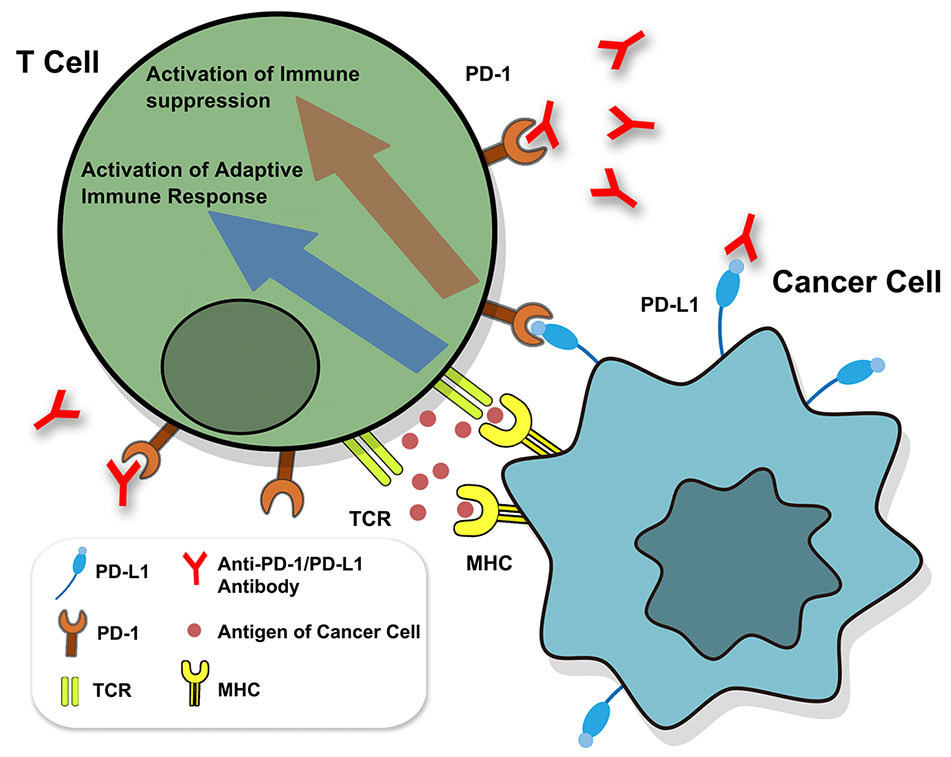
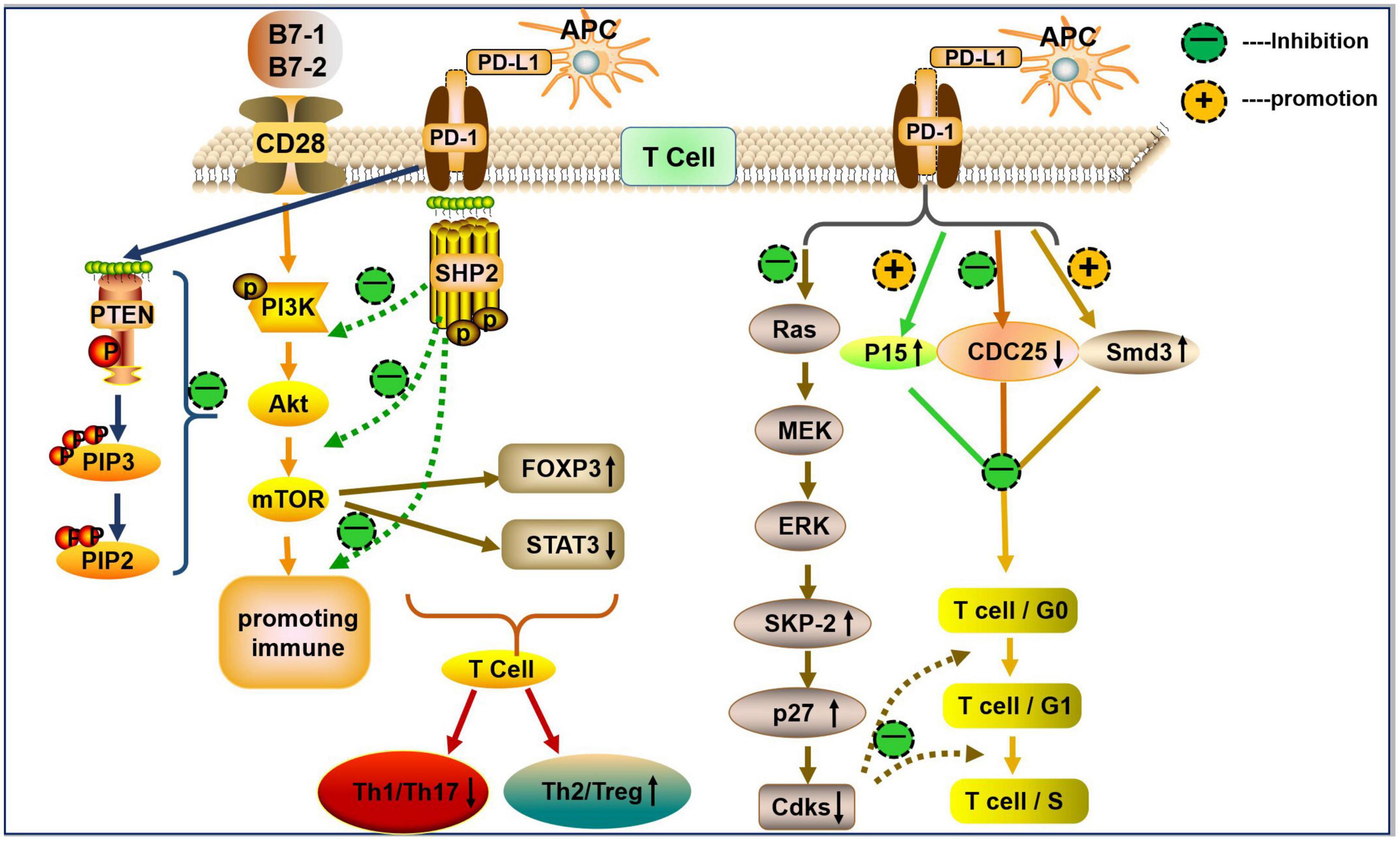
PD-1, or programmed cell death protein 1, plays a crucial role in the regulation of our immune system. It is a receptor that is primarily found on T cells, which are a type of immune cell. The main function of PD-1 is to prevent excessive activation and maintain balance within our immune response.
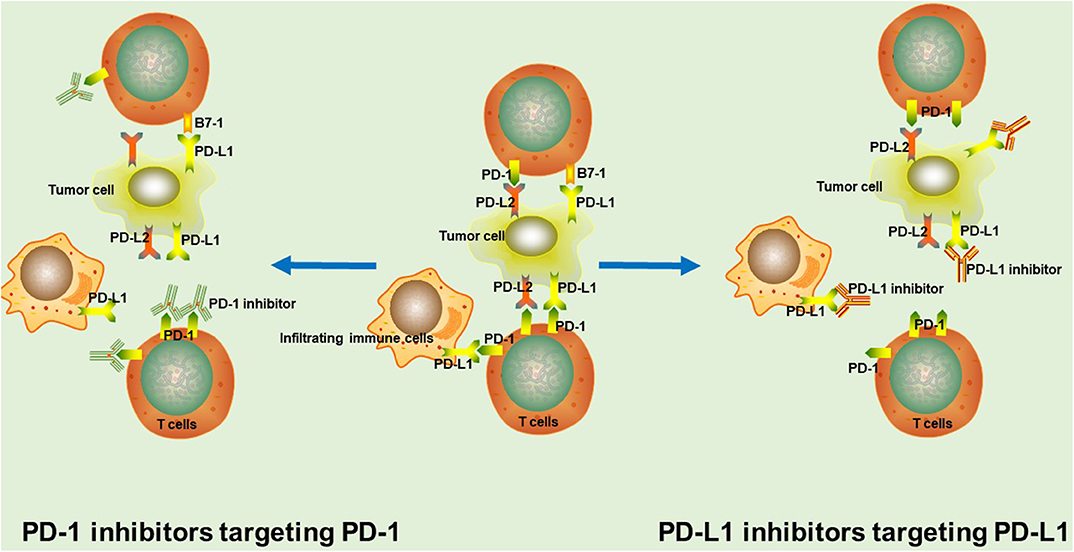
When PD-1 is activated by its ligands, known as PD-L1 and PD-L2, it acts as a checkpoint that dampens the activity of T cells. This mechanism helps in preventing unnecessary inflammation and autoimmune reactions. By inhibiting T-cell activity when needed, PD-1 ensures that our immune system does not go into overdrive and attack healthy tissues.
PD-L1 and PD-L2 are proteins that are expressed on various cells in our body, including cancer cells. When these proteins bind with PD-1, they send a signal to the T cells to slow down their activity. This signaling process is essential for maintaining self-tolerance and preventing the immune system from mistakenly attacking healthy cells.
The significance of understanding the role of PD-1 lies in its implications for immunotherapy. Scientists have developed antibodies called PD-1 agonists that can block the interaction between PD-1 and its ligands. By doing so, these antibodies unleash the full potential of T-cell activity against cancer cells.
Immunotherapies utilizing PD-1 agonist antibodies have shown promising results in treating various types of cancers. These treatments help to “release the brakes” on the immune system, allowing it to mount a more effective attack against tumor cells.
In summary, PD-1 serves as an important regulator in our immune system by preventing excessive activation and maintaining balance. Its interaction with ligands like PD-L1 and PD-L2 acts as a checkpoint to prevent unnecessary inflammation and autoimmune reactions.
Understanding this role has paved the way for innovative immunotherapies that target PD-1 and harness the power of our immune system to fight cancer.
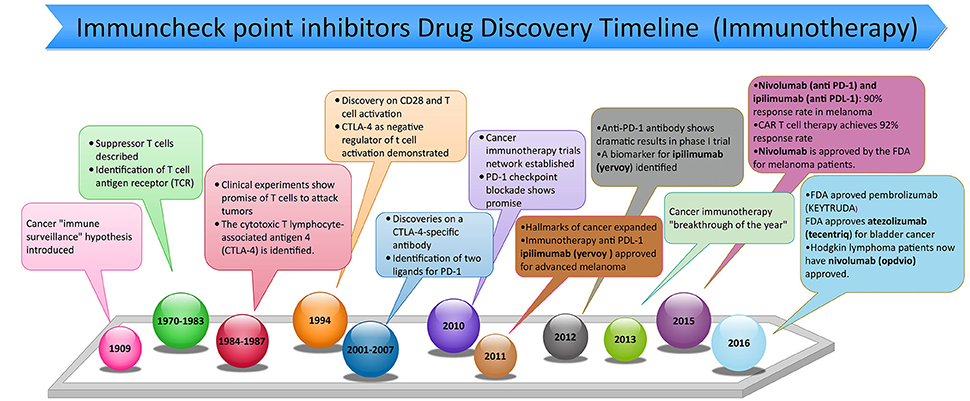
The Breakthrough Discovery of PD-1 Agonist Antibodies
PD-1 agonist antibodies have emerged as a significant breakthrough in cancer immunotherapy. Through extensive research, scientists discovered that certain tumors exploit the PD-1 pathway to evade immune surveillance. This led to the exploration of PD-1 agonist antibodies as a means to reactivate and enhance the immune response against cancer.
Promising results from preclinical studies, where these antibodies demonstrated their ability to boost immune responses and inhibit tumor growth in animal models, paved the way for clinical trials.
Remarkable outcomes were observed in human patients with various types of cancers, including significant tumor shrinkage in those who had exhausted all other treatment options.
The success of these trials has made PD-1 agonist antibodies an integral part of modern immunotherapy approaches. Ongoing research continues to explore novel combinations and dosing regimens to maximize their potential benefits in treating different types of cancer.
Mechanism of Action and Benefits of PD-1 Agonist Antibodies
PD-1 agonist antibodies enhance the immune response by blocking the interaction between PD-1 receptors on T cells and ligands on cancer cells. This releases the brakes on T-cell activity, allowing them to mount a robust immune response against cancer cells.
These antibodies also overcome tumor-induced suppression by restoring T-cell function and enabling them to target and eliminate cancerous cells efficiently. Overall, PD-1 agonist antibodies hold promise in improving cancer treatment outcomes by empowering the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells effectively.
Current Applications and Success Stories
PD-1 agonist antibodies, such as Keytruda, have revolutionized cancer treatment. In advanced melanoma, Keytruda has shown unprecedented response rates and prolonged survival in patients who had exhausted other options. One remarkable case study is Sarah, who achieved complete remission after starting Keytruda treatment.
This success led to accelerated approval for melanoma treatment. PD-1 agonists have also improved outcomes in lung cancer, especially in patients with high PD-L1 expression. Ongoing research explores their potential in bladder, kidney, head and neck cancers, showing promising early results.
PD-1 agonist antibodies are transforming the treatment landscape across different types of cancer.
Limitations, Side Effects, and Challenges
The use of PD-1 agonist antibodies in cancer treatment has brought immense promise, but it also comes with limitations and potential side effects. These therapies can inadvertently trigger immune-related adverse events (irAEs), where the immune system attacks healthy tissues.
Prompt identification and management of these side effects are crucial for patient safety.
Researchers are exploring strategies to minimize irAEs while maintaining efficacy. This includes identifying biomarkers, optimizing dosing regimens, and combining PD-1 agonists with other therapies for a more targeted immune response.
Resistance and lack of response to PD-1 agonist antibodies pose challenges in personalized cancer treatment. Factors such as tumor heterogeneity and alterations in immune checkpoint pathways contribute to resistance. Combination therapies and biomarker identification are being investigated to overcome these challenges.
In summary, addressing the limitations, side effects, and challenges associated with PD-1 agonist antibodies is crucial. Strategies to mitigate side effects, overcome resistance, and improve patient outcomes are actively being pursued.
Future Perspectives and Investment Opportunities
The field of immuno-oncology is experiencing tremendous growth, driven by the success of PD-1 agonist antibodies and other immunotherapies. As more approvals are granted and ongoing research continues, there is a rising demand for innovative therapeutic options.
This presents exciting investment opportunities for those looking to capitalize on this trend.
Investors can explore companies involved in the development of PD-1 agonist antibodies and related technologies. These companies are at the forefront of immuno-oncology, conducting groundbreaking research and clinical trials.
By identifying promising companies with robust pipelines and innovative approaches, diligent investors have the potential to drive significant value in the future.
One area of interest lies in exploring potential new indications and combination therapies for PD-1 agonist antibodies. Beyond their established efficacy in melanoma and lung cancer treatment, researchers are now investigating their potential in breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and even rare malignancies.
Clinical trials are underway to evaluate their effectiveness in these areas. Furthermore, combining PD-1 agonists with other immunotherapies or targeted therapies shows promise for unlocking synergistic effects across various cancer types.
Investing in companies developing PD-1 agonist antibodies not only supports their development but also provides an opportunity to contribute to the advancement and commercialization of these groundbreaking treatments.
By carefully evaluating the track record, pipeline, and innovative strategies of these companies, investors can make informed decisions that align with their investment goals.
In summary, the growing market for immuno-oncology therapies offers promising future perspectives and investment opportunities. The success story of PD-1 agonist antibodies has positioned them as a key player in this rapidly evolving field.
Exploring new indications, combination therapies, and investing in companies at the forefront of research allows investors to take part in shaping the future of cancer treatment while potentially reaping substantial financial rewards.
Conclusion
[lyte id=’SNLr2hqJlrY’]