In the field of investing, it’s important to stay informed about new developments and breakthroughs in various industries. One such development that has caught the attention of investors and those interested in learning more about investing is the Mirati KRAS G12C inhibitor.
This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of this inhibitor, its mechanism of action, preclinical and clinical development, efficacy and safety profile, potential applications and future directions, market potential and competitive landscape, as well as the risks and challenges associated with its development.
By the end of this article, readers will have a clear understanding of the promising future that targeting the KRAS G12C mutation with Mirati’s inhibitor holds.
Overview of the Mirati KRAS G12C Inhibitor
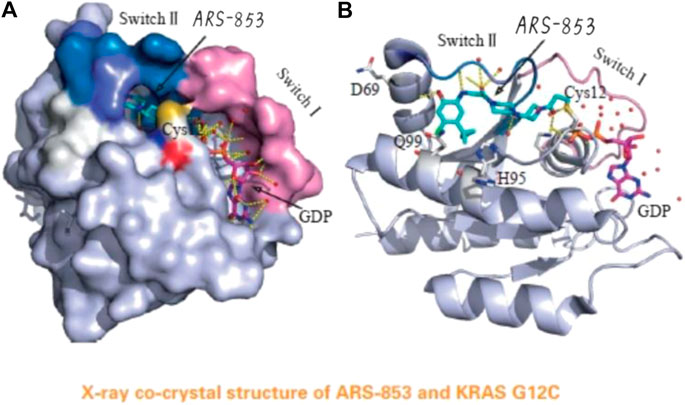
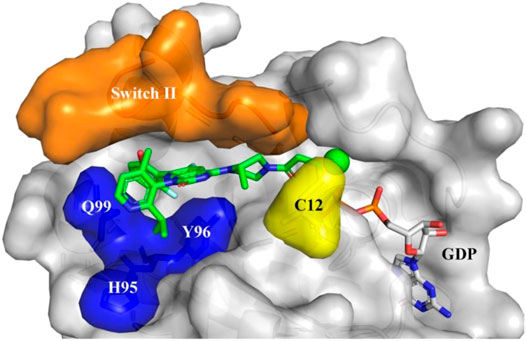
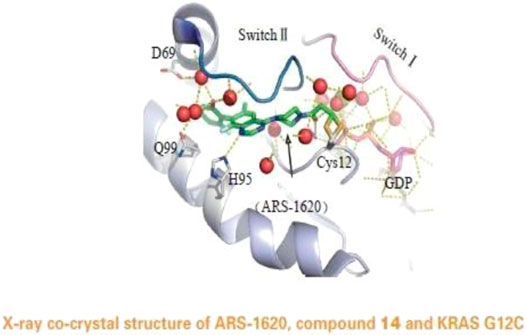
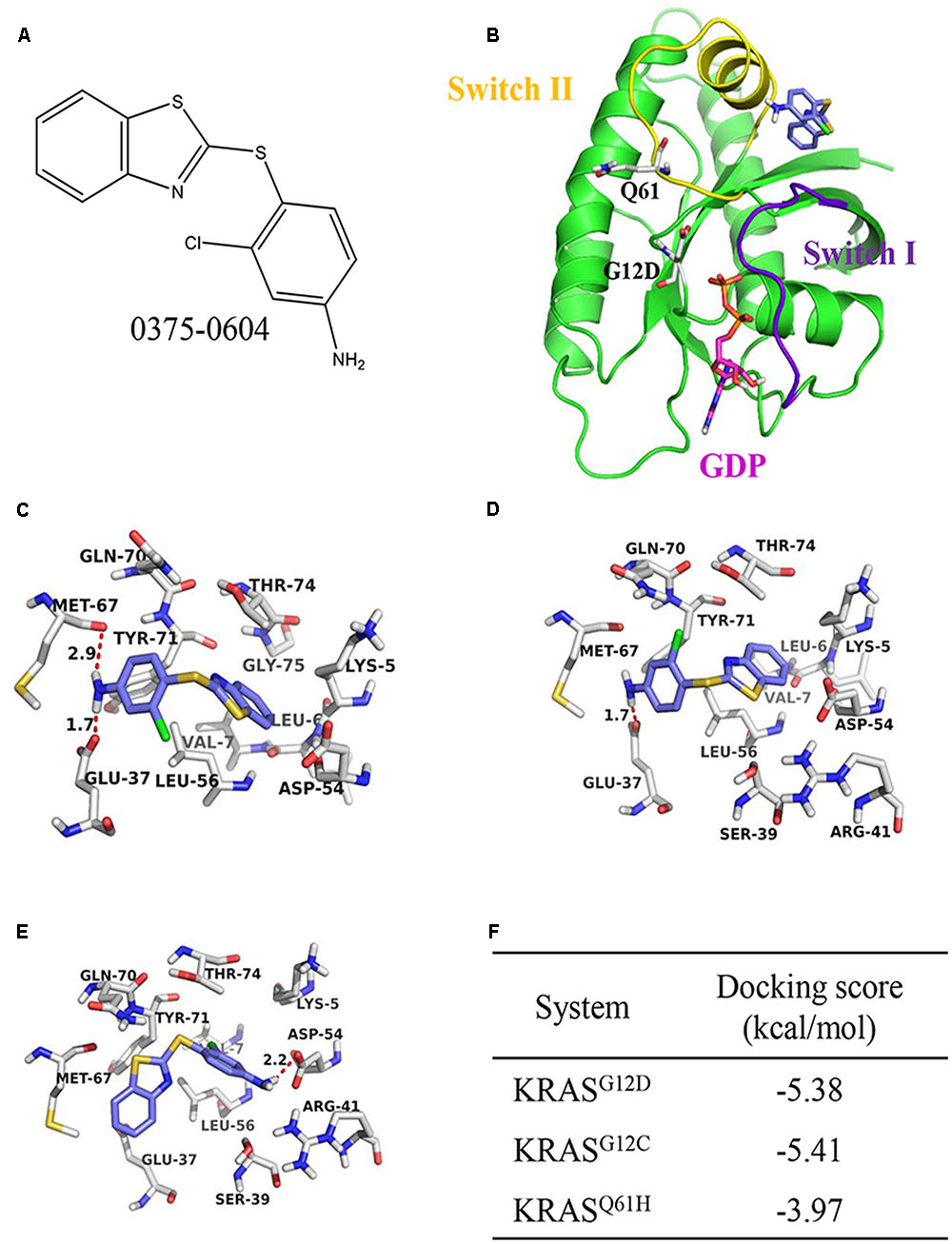
The Mirati KRAS G12C inhibitor is a groundbreaking drug designed to target a specific mutation called KRAS G12C found in certain cancers. It selectively binds to the mutated protein produced by the KRAS gene, inhibiting its activity. This targeted approach minimizes side effects on healthy cells and shows promise for personalized medicine.
The inhibitor offers hope for improved outcomes and prolonged survival rates in patients with this mutation.
Importance of Targeting the KRAS G12C Mutation
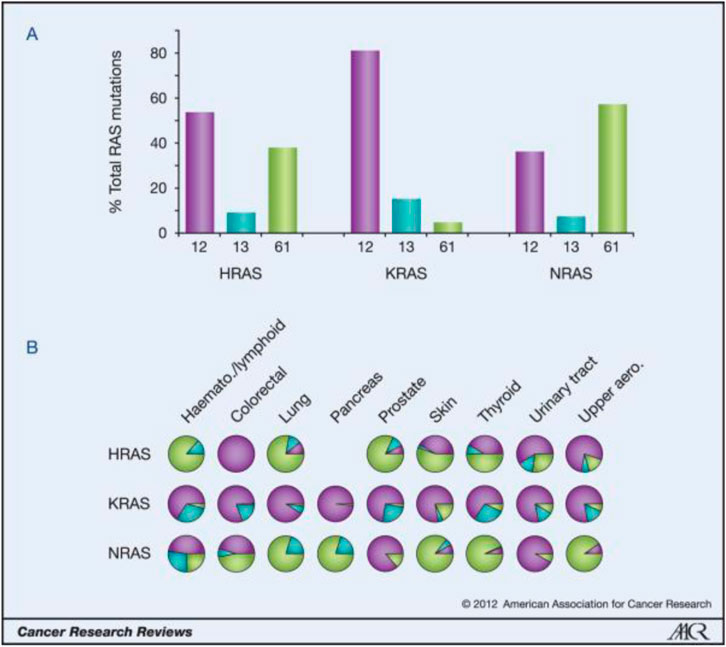
Targeting the KRAS G12C mutation is crucial as it drives tumor growth and survival in various cancers. Developing drugs to inhibit this mutant form of the KRAS protein has historically been challenging due to its complex structure and lack of suitable binding sites.
However, recent advancements in drug discovery technologies have allowed for the development of inhibitors, like Mirati’s, that specifically target this mutation. By focusing on KRAS G12C, researchers aim to disrupt aberrant signaling pathways and offer new treatment options for patients with limited options and poor prognosis.
This targeted approach shows promise in improving outcomes for patients with KRAS G12C-mutated cancers.
Targeting the KRAS G12C Mutation
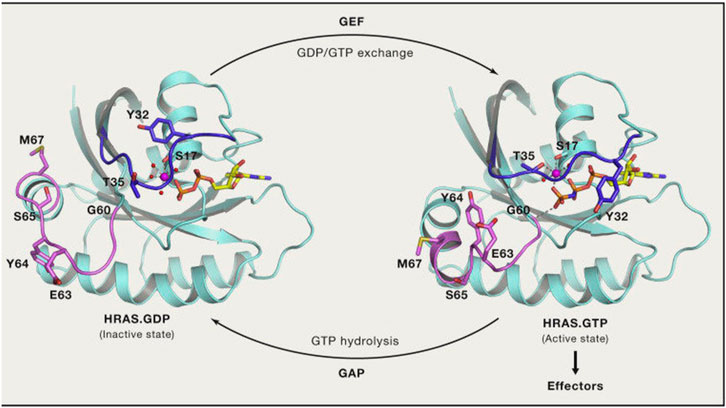
The Mirati KRAS G12C inhibitor is a groundbreaking treatment that specifically targets the KRAS G12C mutation found in various cancers. By binding to the mutated form of the KRAS protein, it disrupts key signaling pathways responsible for promoting tumor growth and survival.
Unlike traditional treatments, this inhibitor selectively affects cancer cells while sparing normal cells, reducing potential side effects. This targeted therapy offers hope for patients with KRAS G12C-mutated cancers, providing a more effective and personalized approach to treatment.
Ongoing research and clinical trials continue to explore its full potential.
Inhibiting Tumor Growth and Promoting Cell Death
The development of the Mirati KRAS G12C inhibitor has shown promising results in inhibiting tumor growth and promoting cell death specifically in cancer cells that harbor this mutation.
By targeting the KRAS G12C mutation, this inhibitor effectively disrupts the signaling pathway that drives uncontrolled cell growth and proliferation in these cancer cells.
Studies have demonstrated that treatment with the Mirati inhibitor leads to a significant decrease in cancer cell proliferation. This is achieved by blocking the aberrant activity of the mutated KRAS protein, which is known to play a critical role in fueling tumor growth.
By inhibiting this key driver of oncogenesis, the Mirati inhibitor offers a potential solution for patients with KRAS G12C-mutated cancers.
Furthermore, the Mirati inhibitor has also been found to promote programmed cell death, or apoptosis, in cancer cells carrying the KRAS G12C mutation. Apoptosis is an essential biological process that allows for the controlled elimination of damaged or abnormal cells.
By enhancing apoptosis in cancer cells, the Mirati inhibitor not only halts tumor growth but also aids in eliminating these harmful cells from within the body.
The promising preclinical and clinical data surrounding the development of this targeted therapy demonstrates its potential as an effective treatment option for patients with KRAS G12C-mutated cancers.
The ability to inhibit tumor growth while simultaneously promoting cell death provides hope for improved outcomes and increased survival rates among individuals affected by these specific types of cancers.
In summary, through its precise targeting of the KRAS G12C mutation, the Mirati inhibitor offers a powerful approach to combating tumor growth and enhancing programmed cell death in cancer cells.
The potential therapeutic benefits of this targeted therapy highlight its significance as a valuable addition to existing treatment options for patients with KRAS G12C-mutated cancers.
Overview of Preclinical Studies and Early Development
Before progressing to clinical trials, extensive preclinical studies were conducted on Mirati’s KRAS G12C inhibitor. These studies evaluated its safety, efficacy, and anti-tumor activity using laboratory and animal models.
Positive results from these studies paved the way for further development of the inhibitor, demonstrating its potential as a promising therapeutic option.
Progression to Clinical Trials and Study Design
After successful preclinical studies, Mirati’s KRAS G12C inhibitor entered clinical trials to assess its safety, dosage requirements, and potential efficacy in human subjects. Phase I trials focused on determining appropriate dosing regimens and identifying any adverse effects.
Subsequent phases aimed to evaluate the drug’s effectiveness in larger patient populations. Throughout the trials, researchers closely monitored both efficacy and safety profiles to ensure optimal therapeutic benefits with minimal risks.
This progression from preclinical studies to clinical trials is a crucial step in bringing new treatments to market, providing valuable data for regulatory approval and further exploration of the drug’s potential.
Results from Phase I Trials on Safety and Tolerability
Preliminary findings from Phase I trials of the Mirati KRAS G12C inhibitor have provided encouraging insights into its safety and tolerability. Throughout the trials, the drug demonstrated a promising safety profile, with manageable side effects that were predominantly mild to moderate in severity.
These results indicate that the inhibitor holds potential for long-term usage without inflicting significant harm on patients.
The Mirati KRAS G12C inhibitor has been well-tolerated by participants in the Phase I trials. The occurrence of adverse reactions was generally low, with most side effects being mild or moderate in intensity.
This is particularly promising as it suggests that patients can receive treatment with this inhibitor without experiencing severe discomfort or complications.
In terms of specific side effects observed during the trials, common occurrences included fatigue, nausea, diarrhea, and headache. These side effects were typically temporary and easily managed through appropriate medical intervention or adjustments in dosing.
Importantly, no life-threatening adverse events were reported during the trials, further supporting the positive safety profile of the Mirati KRAS G12C inhibitor.
These preliminary results are crucial for advancing research and development efforts surrounding this novel drug. By establishing its safety and tolerability early on, researchers can confidently proceed to subsequent phases of clinical trials aimed at assessing efficacy against KRAS G12C-mutant cancers.
This progress brings hope to patients battling these types of cancer and their healthcare providers who are eager to explore new therapeutic options.
Initial Signs of Efficacy Observed in Phase I Trials
Phase I trials for the treatment of KRAS G12C-mutated NSCLC have shown promising early signs of efficacy, alongside a favorable safety profile. These initial indications provide hope for future treatment options for patients with this specific mutation.
One notable finding from these trials is the observed tumor shrinkage in patients who received the inhibitor. This suggests that the targeted therapy has the potential to effectively combat the growth and spread of cancer cells in individuals with KRAS G12C-mutated NSCLC.
Tumor shrinkage is a crucial measure of treatment effectiveness, as it indicates a reduction in the size of tumors, which can alleviate symptoms and improve overall patient outcomes.
Furthermore, prolonged periods of disease control have been observed in patients participating in Phase I trials. Disease control refers to maintaining stability and preventing progression of cancer.
The fact that these patients experienced extended periods without disease advancement is an encouraging sign that the inhibitor may help manage KRAS G12C-mutated NSCLC successfully.
It is important to remember that Phase I trials primarily focus on evaluating safety rather than efficacy. However, these preliminary findings suggest that this particular inhibitor holds promise as an effective treatment option for patients with KRAS G12C-mutated NSCLC.
Further research and clinical trials will be necessary to confirm its long-term efficacy and establish its place in standard treatment protocols.
[lyte id=’HjOzirGlimk’]