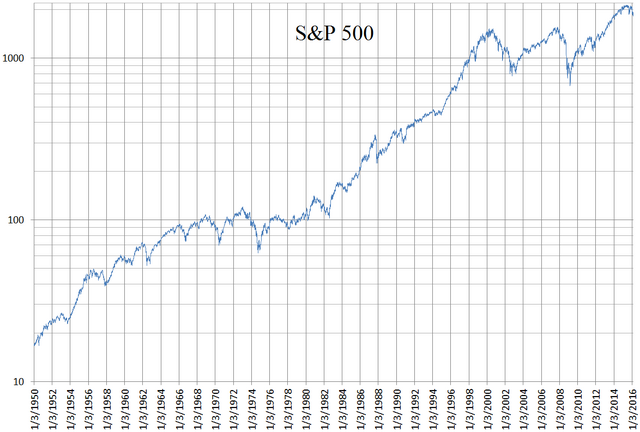
Investing in the stock market can be a daunting task, especially for beginners. With so many indices and investment options available, it’s important to understand the basics before diving in. One index that often grabs the attention of investors is the S&P 500.
In this article, we will explore what the S&P 500 is, how it is calculated, its historical significance, and its benefits and risks as an investment option.
So let’s dive right in and discover everything you need to know about the interactive world of the S&P 500!
Introduction to the S&P 500
The S&P 500 is a widely recognized stock market index that tracks the performance of 500 large-cap companies listed on US stock exchanges. It serves as a benchmark for measuring the health of the US stock market and provides valuable insights into overall company performance.
Calculated using a market capitalization-weighted approach, it reflects changes in both price and outstanding shares. Investors often use it as a reference point for evaluating portfolio performance, and financial products like ETFs and mutual funds are designed to track its movements.
Understanding the S&P 500 is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
Historical Overview of the S&P 500
The S&P 500, introduced by Standard & Poor’s Corporation on March 4, 1957, is a significant index in the financial world. Initially consisting of 425 stocks, it gradually expanded over time to include more companies.
Created to provide investors with a comprehensive benchmark reflecting market performance and economic trends, the S&P 500 has become synonymous with measuring the pulse of the U.S. economy. Its diverse representation of various industries and sectors offers a reliable gauge for assessing market conditions.
Today, it is widely regarded as one of the most accurate reflections of overall U.S. equity performance.
| Date Introduced | March 4th, 1957 |
|---|---|
| Initial Stocks Included | 425 |
| Current Number of Stocks | Varies, approximately 500 |
| Purpose | Broad-based benchmark, indicator for economic trends |
| Importance | Reflects market performance, guides investment decisions |
Table: Key Information about the S&P 500
Components and Weighting of the S&P 500
The S&P 500 consists of a diverse range of companies from sectors like technology, finance, healthcare, consumer goods, and more. Well-known names such as Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, and Facebook are among its constituents. The weight of each company in the index is determined by its market capitalization.
This means that larger companies have a greater influence on the index’s performance compared to smaller ones. This approach provides investors with insights into market trends across sectors and helps evaluate investment strategies.
The S&P 500’s composition and weighting system make it an essential benchmark for monitoring overall market health and understanding economic trends.
In summary, the S&P 500 includes a variety of companies from different industries and weights them based on their market value. This allows investors to assess market trends and make informed investment decisions.
Performance and Tracking of the S&P 500
The performance of the S&P 500, a key benchmark index for the U.S. stock market, has delivered impressive average annual returns over several decades. Despite year-to-year variations, historical data shows that investing in this index has generally been profitable in the long term.
The S&P 500’s performance is influenced by various factors such as economic conditions, geopolitical events, government policies, and technological advancements. Recessions and corporate scandals can significantly impact its performance, while positive developments like advancements in renewable energy or medical research can boost certain sectors.
To make informed investment decisions, it’s important to monitor economic indicators, stay updated on geopolitical developments and policy changes, and consider technological advancements. By understanding these influences on the S&P 500’s performance, investors can navigate the stock market more effectively.
Benefits and Risks of Investing in the S&P 500
Investing in the S&P 500 provides several advantages. It offers broad exposure to various industries and sectors, simplifying portfolio diversification without selecting individual stocks. The index’s high liquidity ensures easy buying and selling of shares.
Additionally, as a widely followed stock market barometer, the S&P 500 reflects investor sentiment and economic trends. However, investors should be aware of potential risks such as market volatility and capital loss.
Alternatives to Consider Alongside or Instead of the S&P 500
While the S&P 500 is a popular choice for many investors, exploring other indices can offer unique opportunities and diversification. The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) tracks 30 large-cap companies, providing insight into established players across industries.
The Nasdaq Composite Index (NASDAQ) focuses on technology and growth-oriented companies, while the Russell Indexes offer various subsets tracking different segments of the US stock market.
Considering these alternatives alongside or instead of the S&P 500 allows investors to tailor their portfolios and potentially capitalize on different sectors and strategies. Diversify your investments and enhance returns by exploring these alternative indices.
Conclusion and Key Considerations for Investing in the S&P 500
[lyte id=’mspM8ksEPH4′]