In the world of cancer treatment, new breakthroughs and advancements are constantly being made. One such advancement is the use of Cetuximab in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). NSCLC is a type of lung cancer that accounts for about 85% of all cases, making it a significant concern for both patients and healthcare professionals.
But what exactly is Cetuximab, and how does it impact the treatment of NSCLC? In this article, we will delve into the details of this innovative drug, exploring its potential benefits and implications for those affected by this devastating disease.
What is Cetuximab?
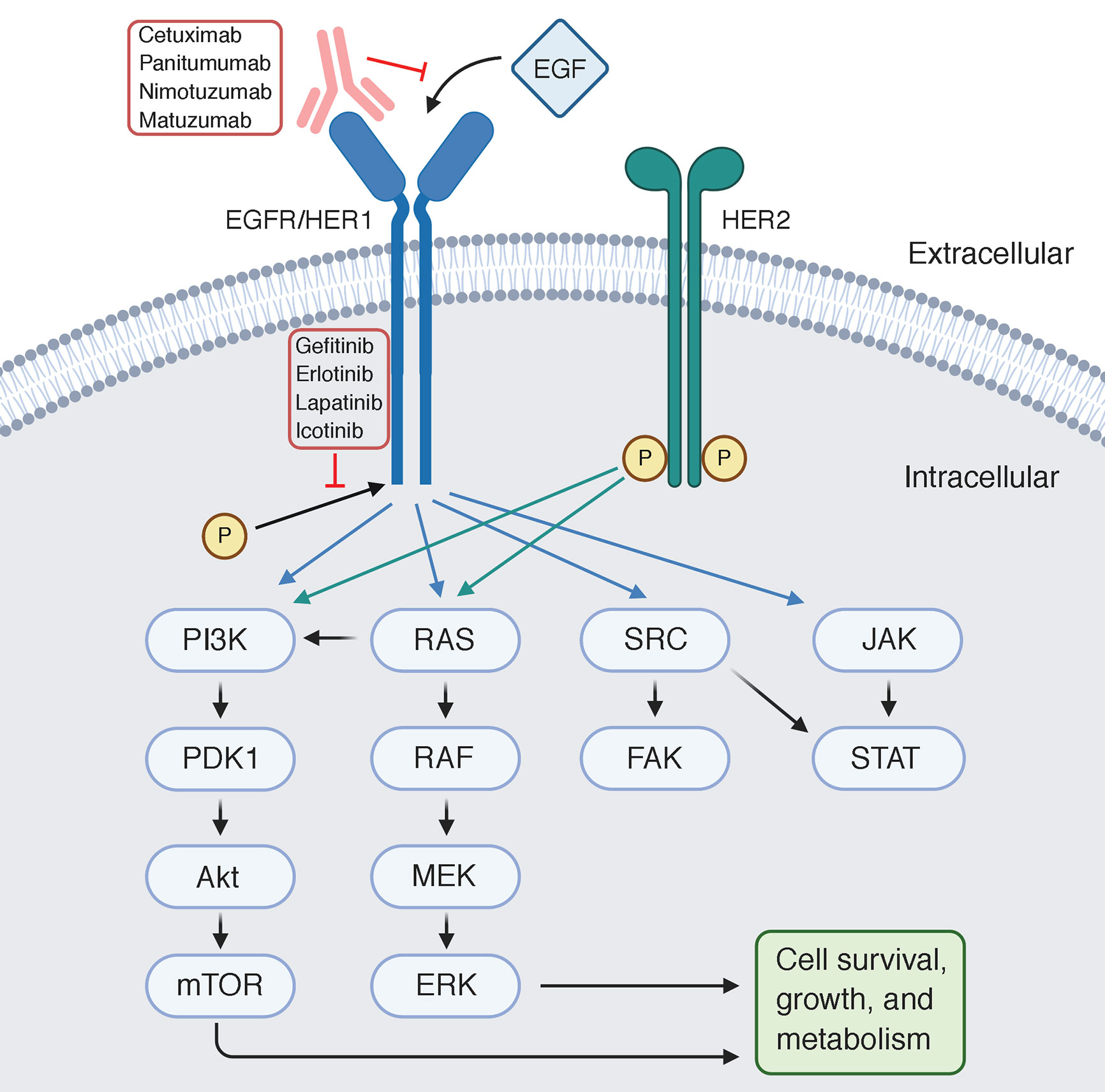
Cetuximab is a targeted therapy that belongs to the class of drugs known as monoclonal antibodies. It works by inhibiting the protein called epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which plays a crucial role in the growth and spread of cancer cells.
By blocking EGFR, Cetuximab helps slow down or stop tumor growth in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). It is often used in combination with other treatments like chemotherapy or radiation therapy for maximum effectiveness.
Through its precise targeting and disruption of tumor-promoting mechanisms, Cetuximab offers new hope in the fight against cancer.
Overview of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC)
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is a prevalent form of lung cancer characterized by abnormal cell growth in the lungs. It accounts for approximately 85% of all lung cancer cases and is classified into subtypes such as adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and large cell carcinoma.
NSCLC can be caused by factors like smoking, exposure to chemicals or pollutants, and genetic mutations. Historically, NSCLC had a poor prognosis due to late-stage diagnosis and limited treatment options. However, advancements in medical research have brought hope for improved outcomes.
Targeted therapies like Cetuximab show promise in treating specific NSCLC subtypes. Cetuximab is an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) inhibitor that blocks signals promoting cancer cell growth.
Clinical trials combining Cetuximab with chemotherapy drugs or radiation therapy have shown potential in improving survival rates and progression-free survival.
Phase I/II trials specifically focusing on Cetuximab’s impact on NSCLC are conducted to assess its safety and effectiveness across different stages and subtypes of the disease. These trials evaluate patient responses by analyzing tumor shrinkage and duration of response.
In the next section, we will explore the findings of Phase I/II trials of Cetuximab in NSCLC, providing insights into its efficacy, side effects, and overall impact on patient outcomes. These trials aim to establish Cetuximab as a valuable treatment option for NSCLC patients, offering new hope in their battle against this challenging disease.
Background and Rationale for Using Cetuximab in NSCLC Treatment
The treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) has seen significant advancements in recent years, with targeted therapies emerging as promising options. One such therapy is Cetuximab, which has shown potential in improving outcomes for patients with NSCLC.
Cetuximab works by targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), a protein that is often overexpressed in lung cancer cells. This overexpression of EGFR is associated with increased tumor growth, invasion, and resistance to chemotherapy.
By specifically targeting EGFR, Cetuximab aims to disrupt these processes and enhance the effectiveness of NSCLC treatment.
To determine the safety and efficacy of Cetuximab in combination with standard chemotherapy regimens for advanced NSCLC, researchers conducted Phase I/II trials. These trials aimed to identify the optimal dosage of Cetuximab and assess any potential side effects or adverse events associated with its use.
The rationale behind using Cetuximab lies in its ability to directly inhibit EGFR signaling pathways that play a critical role in promoting cancer cell proliferation and survival. By blocking this pathway, Cetuximab seeks to halt the progression of NSCLC and improve patient outcomes.
The results from these trials have been encouraging, demonstrating that the addition of Cetuximab to standard chemotherapy regimens can lead to improved response rates and prolonged survival for patients with advanced NSCLC. However, it is important to note that individual patient characteristics may influence the response to Cetuximab therapy.
Results and Findings from Phase I/II Trials
Phase I/II trials have shown that adding Cetuximab to standard chemotherapy regimens for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) leads to improved response rates and overall survival compared to chemotherapy alone. The addition of Cetuximab has been well-tolerated, with manageable side effects such as skin rash, diarrhea, and infusion reactions.
These findings suggest that Cetuximab is a valuable treatment option against NSCLC.
Phase III Trials in Advanced NSCLC
Phase III trials are being conducted to further evaluate the effectiveness and safety of Cetuximab in advanced NSCLC. These larger-scale studies aim to compare the outcomes of patients receiving Cetuximab combined with standard chemotherapy versus those treated with other therapies.
The results will provide more robust evidence on the efficacy and potential role of Cetuximab in the standard treatment approach for advanced NSCLC.
Importance of Phase III Trials in Evaluating Efficacy and Safety
Phase III trials are crucial in determining whether a new treatment option, like Cetuximab, should be widely approved. These trials compare the effectiveness and safety of the investigational drug with the current standard of care, using larger patient populations.
The goal is to provide robust evidence that influences treatment guidelines and helps healthcare professionals make informed decisions about incorporating Cetuximab into their treatment plans.
Phase III trials play a vital role in evaluating the benefits, risks, and comparative effectiveness of Cetuximab for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Overview of Key Phase III Trials Involving Cetuximab in Advanced NSCLC
Cetuximab has been extensively studied in Phase III trials for its effectiveness and safety in treating advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). One notable trial, the FLEX study, compared Cetuximab plus chemotherapy to chemotherapy alone as a first-line treatment option for advanced NSCLC patients.
Results showed that patients receiving the combination had improved overall survival, especially those with high EGFR expression levels. This highlights the importance of personalized medicine in NSCLC treatment.
Efficacy and Safety Profile of Cetuximab in NSCLC Treatment
Cetuximab has shown consistent efficacy in improving outcomes for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients. When added to standard chemotherapy regimens, it increases response rates and overall survival, especially in patients with high EGFR expression levels.
Additionally, its safety profile is favorable, with manageable side effects that can be addressed by healthcare professionals. This combination of efficacy and tolerability makes Cetuximab an attractive option for optimizing NSCLC treatment strategies.
Implications for Clinical Practice and Future Research
The findings from clinical trials suggest that Cetuximab holds great promise in the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). By specifically inhibiting EGFR, a protein that plays a key role in tumor growth and progression, Cetuximab offers a personalized approach to patient care.
Further research is needed to explore optimal dosages, identify predictive biomarkers, and investigate potential combinations with other therapies. By expanding our knowledge of Cetuximab’s efficacy and safety profile, we can refine treatment strategies and pave the way for improved outcomes in NSCLC patients.
Establishing guidelines for its appropriate use, defining patient selection criteria, and monitoring for adverse effects are essential steps in implementing Cetuximab in clinical practice. Additionally, future research should focus on different NSCLC subtypes and explore novel combination therapies to enhance treatment responses.
Collaboration between researchers, clinicians, and pharmaceutical companies is crucial to expedite the translation of scientific discoveries into clinical practice. Together, we can continue to innovate and improve the lives of NSCLC patients through advancements in Cetuximab treatment options.
[lyte id=’zKuSk0qPAkY’]