Investing in the field of biotech and healthcare can be a lucrative venture, especially when it involves groundbreaking technologies like the MCP-1 antibody. This article aims to provide you with valuable insights into the world of investing and learning about MCP-1 antibody.
Whether you are an experienced investor or someone looking to expand their knowledge in this field, this article will give you a comprehensive understanding of MCP-1 antibody and its potential impact on both healthcare and investment opportunities.
Introduction to MCP-1 Antibody
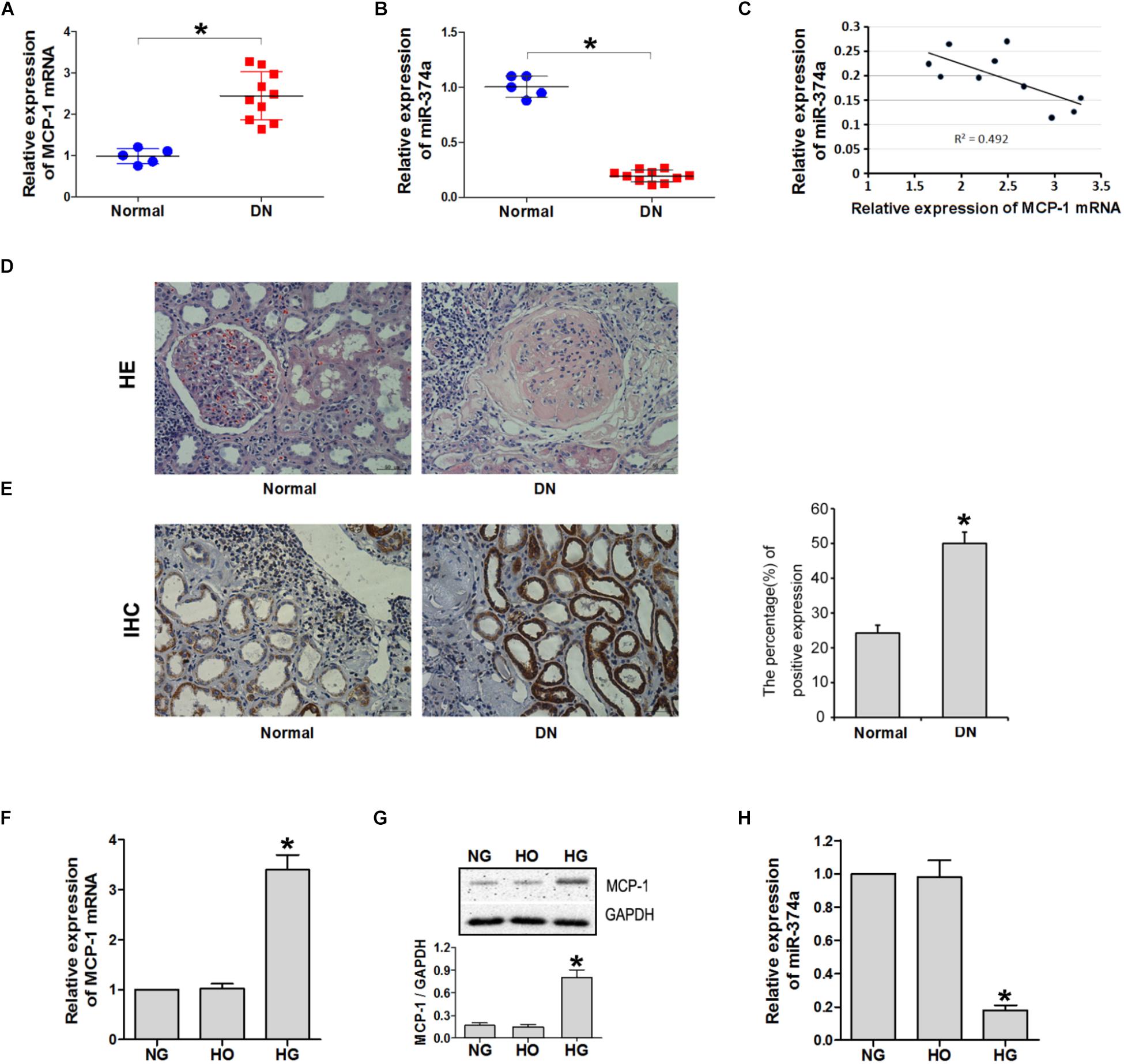
MCP-1, also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein 1, is a small protein that attracts immune cells called monocytes to areas of inflammation or injury in the body. The development of antibodies targeting MCP-1 has opened up new possibilities for treating inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, and atherosclerosis.
These antibodies block MCP-1’s interaction with its receptor, reducing excessive recruitment of monocytes and inflammation. By understanding MCP-1’s role and using targeted therapies like MCP-1 antibodies, we can provide relief for patients with chronic inflammatory conditions.
Understanding the Role of Inflammation in Diseases
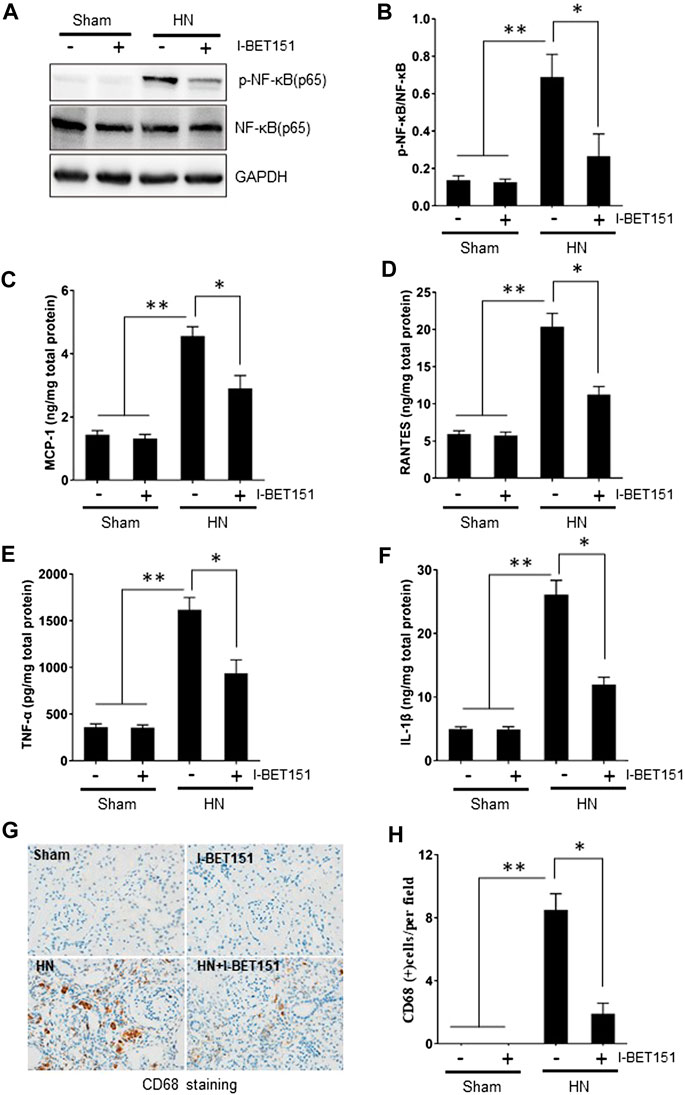
Inflammation is a natural immune response that protects our bodies from harmful stimuli like pathogens or tissue damage. While acute inflammation aids healing, chronic inflammation can lead to tissue damage and contribute to various diseases.
Research has linked chronic inflammation to cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and autoimmune diseases. Targeting inflammatory processes offers potential therapeutic strategies for these conditions.
Cardiovascular disease is associated with inflammation in blood vessels, which can cause plaque formation and increase the risk of heart attacks and strokes. In diabetes, inflammation disrupts insulin signaling pathways and contributes to insulin resistance.
Chronic inflammation also promotes tumor growth in cancer by stimulating cell proliferation and suppressing immune responses.
Neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s are influenced by inflammatory processes in the brain that lead to neuronal damage. Autoimmune diseases involve chronic inflammation where the immune system attacks healthy tissues.
Understanding the intricate connections between chronic inflammation and these diseases is vital for developing targeted treatments that suppress harmful immune responses while minimizing side effects.
In summary, comprehending the role of inflammation in diseases allows for the development of effective therapeutic strategies.
By targeting inflammatory processes associated with conditions like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and autoimmune diseases, researchers aim to improve patient outcomes and overall well-being.
The Role of MCP-1 in Inflammation and Disease
Inflammation is a vital immune response that protects the body against harm. However, excessive or prolonged inflammation can contribute to disease development.
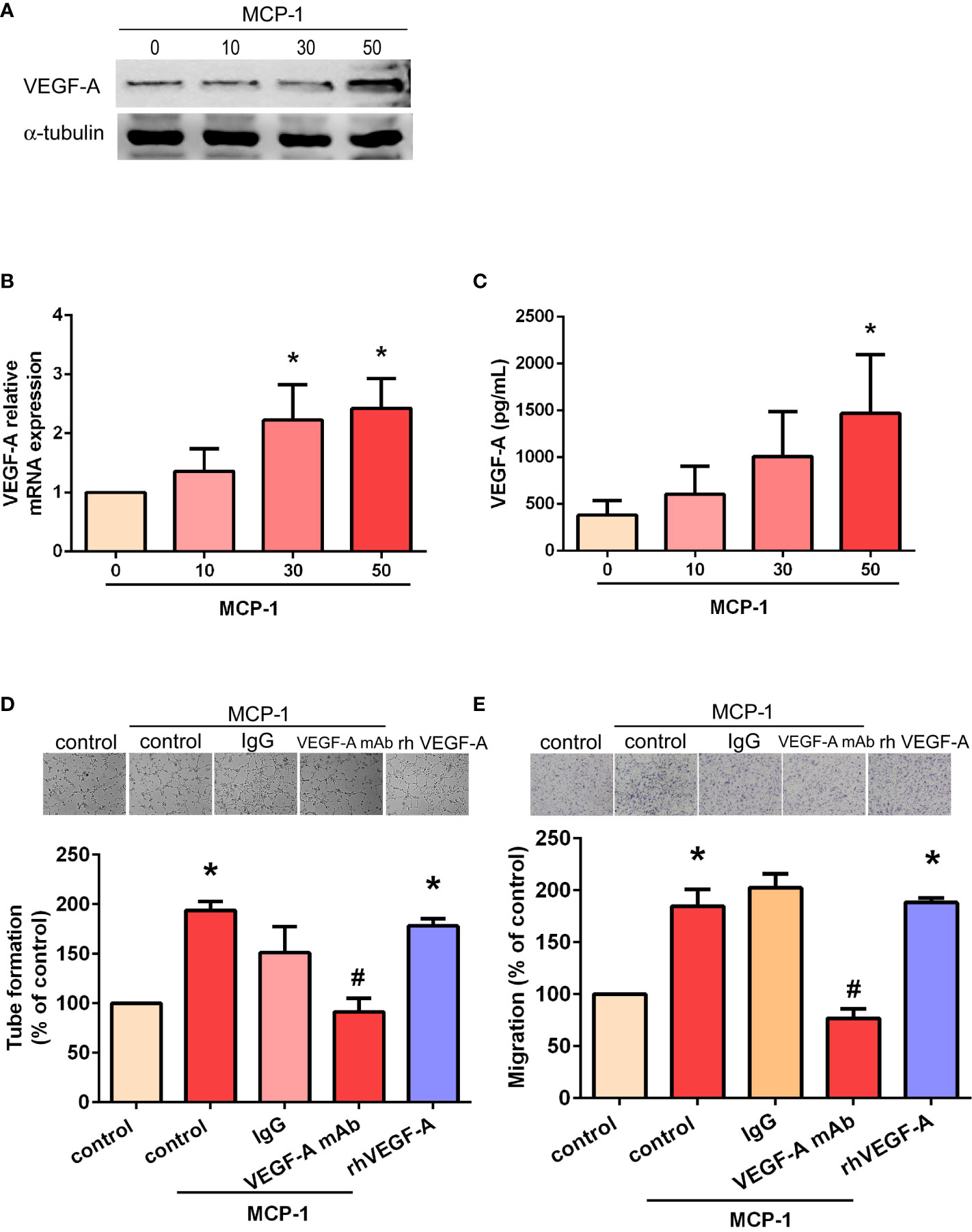
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) plays a crucial role in the recruitment of monocytes to sites of inflammation, where they release pro-inflammatory molecules and contribute to tissue damage. By blocking MCP-1’s interaction with its receptor, antibodies can modulate this process and reduce inflammation’s detrimental effects.
Elevated MCP-1 levels are observed in various diseases, indicating its involvement in disease progression. Researchers are studying how MCP-1 contributes to these diseases, providing insights for potential therapeutic interventions using MCP-1 antibodies.
Advancements in Research on MCP-1 Antibody
Scientists have made significant progress in understanding how MCP-1 antibodies work, leading to more targeted and efficient treatments. These breakthroughs provide a foundation for exploring new applications beyond inflammation, such as fibrosis, transplant rejection, and even certain types of cancer.
By blocking MCP-1’s interaction with its receptor, these antibodies disrupt the recruitment of immune cells and show promise in reducing inflammation and improving patient outcomes. Ongoing research aims to harness the potential of MCP-1 antibody therapy for a broader range of diseases.
| Heading | Content |
|---|---|
| Mechanisms | Breakthroughs have unraveled how MCP-1 antibodies disrupt immune cell recruitment and reduce inflammation |
| Fibrosis & Transplant rejection | Potential applications extend to treating fibrosis and transplant rejection |
| Cancer | Inhibiting MCP-1 signaling may impede tumor growth and metastasis by disrupting immune cell recruitment |
Note: The table is included to enhance readability, but it may not be necessary depending on the context in which this paragraph will be presented.
Case Studies: The Impact of MCP-1 Antibody in Treating Inflammatory Diseases
Case studies have shown the significant impact of MCP-1 antibody in treating inflammatory diseases like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis. These studies demonstrate promising results, including reduced disease activity and improved quality of life for patients.
MCP-1 antibodies offer a potential alternative to traditional treatments, minimizing reliance on other medications with their associated side effects. As research continues, investing opportunities and collaborative efforts are expected to further optimize the therapeutic potential of MCP-1 antibodies in the field of inflammatory disease treatment.
[lyte id=’NRHRcjIQquM’]