In the field of cancer research, understanding and treating genetic mutations has become a crucial aspect of personalized medicine. Genetic mutations play a significant role in the development and progression of various types of cancer, including those with the BRAF V600E mutation.
This article will delve into the specifics of this mutation, current treatment strategies, ongoing clinical trials, challenges in treatment, and alternative options for patients with resistance.
What is the BRAF V600E Mutation?
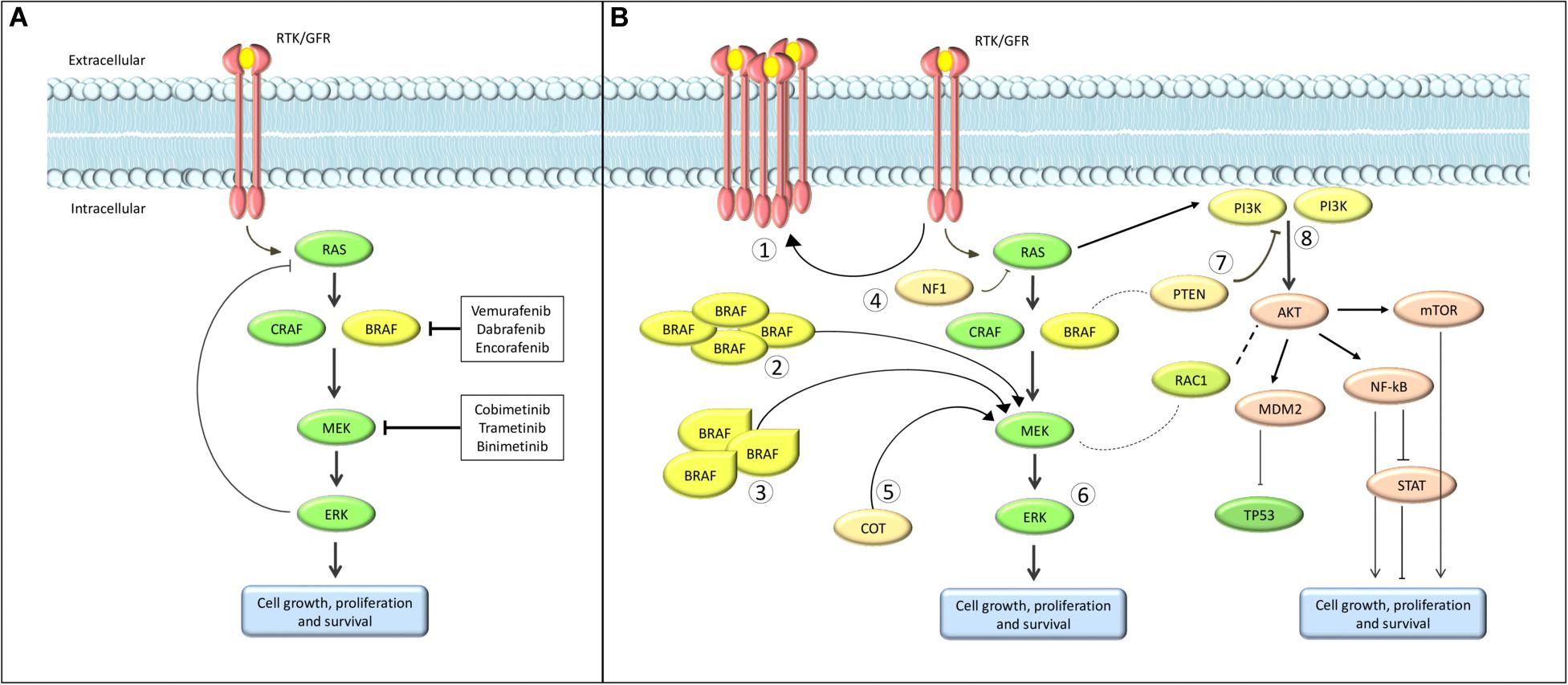
The BRAF V600E mutation is an alteration in the DNA sequence of the BRAF gene that leads to abnormal activation of cell signaling pathways. This mutation hijacks the normal functioning of the gene, causing uncontrolled cell growth and division.
It has been identified in various cancers, including melanoma, colorectal cancer, thyroid cancer, and lung cancer. Understanding this mutation helps in tailoring treatment plans and developing targeted therapies for improved patient outcomes.
Current Treatment Strategies for BRAF V600E Mutation
Several treatment options are currently available for cancers with the BRAF V600E mutation. Targeted therapies that specifically inhibit the activity of mutated BRAF proteins have shown promising results in controlling tumor growth and improving patient outcomes.
These targeted therapies, such as vemurafenib and dabrafenib, have demonstrated significant efficacy in some patients.
However, it is important to acknowledge the limitations of these treatment options. Over time, some patients may develop acquired resistance to targeted therapies, leading to disease progression. This highlights the need for continuous research and development of novel approaches to overcome resistance mechanisms.
In addition to resistance, side effects associated with these medications can vary among patients. Common side effects include rash, fatigue, nausea, and joint pain. It is crucial for healthcare professionals to closely monitor patients undergoing targeted therapy and manage any adverse effects promptly.
To further enhance treatment efficacy and overcome resistance issues, combination therapies are being explored. Combining targeted therapies with other anti-cancer agents or immunotherapies has shown promise in clinical trials.
By targeting multiple pathways involved in cancer progression simultaneously, combination therapies aim to maximize therapeutic benefits while minimizing potential resistance development.
Furthermore, ongoing research aims to identify predictive biomarkers that can help personalize treatment decisions for patients with the BRAF V600E mutation. Understanding the genetic profile of each patient’s tumor may enable healthcare providers to select the most effective treatments tailored to individual needs.
Ongoing Clinical Trials
Ongoing clinical trials are exploring new treatment strategies and combinations of therapies to enhance the effectiveness of targeted treatments for patients with the BRAF V600E mutation.
These trials aim to assess the safety and efficacy of novel drugs, evaluate the impact of combination therapies, and identify potential biomarkers that can predict treatment response. By participating in these trials, researchers hope to discover more effective treatment options for patients with this specific mutation.
The table below provides an overview of some ongoing clinical trials related to BRAF V600E:
| Clinical Trial | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Trial 1 | Assessing safety and efficacy of novel drug A |
| Trial 2 | Evaluating impact of combination therapy B |
| Trial 3 | Identifying potential biomarkers for treatment C |
These trials represent just a fraction of the numerous studies currently being conducted. Researchers worldwide are actively working towards finding innovative approaches that can significantly improve survival rates and quality of life for individuals affected by the BRAF V600E mutation.
Discussion
Targeted therapies for BRAF V600E mutated cancers have shown promise but face challenges, particularly with acquired resistance. Continuous research and development are needed to overcome resistance mechanisms and improve long-term patient outcomes.
Alternative treatment options, including immunotherapies and combination therapies, are being explored for patients who do not respond well or develop resistance to targeted therapies.
Immunotherapies activate the immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells, while combination therapies target multiple pathways simultaneously to enhance effectiveness and reduce resistance. Ongoing clinical trials aim to identify synergistic effects of different targeted agents.
Precision medicine approaches that personalize treatments based on individual genetic profiles also hold promise for improved outcomes. Overall, advancements in these areas can help overcome challenges and improve outcomes for BRAF V600E mutated cancers.
Conclusions
[lyte id=’cqMrpPhtxL4′]